Traditional Chinese Medicine
WHAT IS ACUPUNCTURE?
Acupuncture (from Latin, ‘acus‘ (needle) + ‘punctura‘ (to puncture)) is a comprehensive form of health care that is administered through the insertion of fine needles into the body at specific points that have been shown to be effective in treating specific health issues. Acupuncture has been a part of Traditional Oriental Medicine (Traditional Chinese Medicine) for several thousand years. 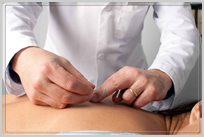
In addition, Traditional Oriental Medicine includes Moxabustion, Acupressure, Herbology, Nutrition, Lifestyle Counseling, Breathing and Movement Exercises applied under the same treatment principles.
HOW DOES IT WORK?
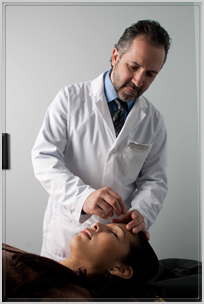
‘Qi’ (pronounced chee) or energy, a bioelectrical concept that differentiates Oriental Medicine from biochemically based Western Medicine was defined by the ancient Chinese to be the vital force essential to the functionality of all life forms. In Traditional Oriental Medicine the smooth and sufficient circulation of Qi and Blood defines our health. Circulation that becomes obstructed inhibits the body’s natural ability to heal itself and disease takes root. Inserting needles into specific acupoints along 14 major meridians, or energy pathways traversing the body regulates the flow of Qi to provide homeostasis or functional balance of the body thereby promoting health. Modern science has been able to measure and confirm these ancient acupoint locations.
A visual inspection of the tongue, palpation of the radial pulse along the wrist and specific questions on the history of your health are combined to form an Oriental Medicine diagnosis of your condition before treatment begins.
ARE THE NEEDLES SAFE? DOES IT HURT? WHAT WILL I FEEL?
Acupuncture needles are completely sterile, disposable and safe under the care of a properly trained acupuncturist. The sensation felt upon needle insertion differs from patient to patient. The needle diameter is comparable to a human hair. Most patients feel nothing at all upon needle insertion, while others may report minor sensations of heaviness, distention, warmth, tingling, or electrical sensation either around the needle or traveling up or down the affected meridian. Most patients feel deeply relaxed and peaceful during their treatment. Occasionally patients will fall asleep and awaken soon after to feel refreshed and energized.
The most frequently needled body regions are below the elbows and knees and along the back, shoulders and abdomen.
Is Acupuncture Safe? – Additional Information
The Safety of Acupuncture & Oriental Medicine, NCCAOM Oct. 8, 2010
Response to British Medical Journal Editorial Regarding Unsafe Practice of Acupuncture, NCCAOM Mar. 8, 2010
HOW MANY TREATMENTS WILL I NEED? CAN IT HELP MY CONDITION?
The number of treatments will depend upon the duration, severity, and nature of your complaint. It is suggested that you try several visits and see how you are doing–at this time a reevaluation can be done and a better analysis can be made. You may need only a single treatment for an acute condition. A series of six to twelve treatments may resolve many chronic problems. Some degenerative conditions may require many treatments over time.
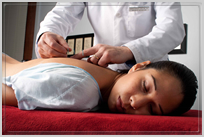
Acupuncture and Oriental Medicine (Traditional Chinese Medicine) is a complete health care system that can affect a patient’s health on many levels physically, emotionally, psychologically, spiritually and energetically.
Oriental Medicine is better suited for chronic degenerative conditions than for acute life threatening illness. Western Medicine provides the best acute trauma care available yet Oriental Medicine is applied extensively in Asia and Europe in hospitals and acute care facilities in conjunction with Western Medicine. Some conditions respond well when Western and Oriental Medicine are combined in a complementary manner.
IS ACUPUNCTURE COVERED BY HEALTH INSURANCE
Some insurance companies do cover acupuncture but coverage can be limited. Acupuncture is typically offered as a rider or an addition to standard coverage. If you pay for your own health insurance it’s easy to inquire and make modifications. It is not a very expensive addition and can prove to be greatly beneficial. More and more insurance companies and employers are recognizing the benefits of acupuncture. You can help make acupuncture more available by petitioning your employer to add acupuncture to their group coverage or insist your personal insurance company offer you reimbursement for acupuncture treatments before you accept their policy.
BEFORE TREATMENT
- Wear loose clothing. Women should not wear one-piece dresses.
- Avoid treatment when excessively fatigued, hungry, or full.
- Avoid alcohol or drug use on the day of your treatment.
- Feel free to ask questions. Understanding your condition will improve treatment results and aid in the prevention of future health issues. We kindly encourage you to participate in your healing process.
To ensure a proper treatment please inform your practitioner of any medications, including supplements and all pre-existing health conditions especially if you are PREGNANT or have a PACEMAKER.
DURING TREATMENT
Simply relax. Ask your practitioner any questions you may have to ensure your comfort.
AFTER TREATMENT
Resting is recommended. Refrain from stressful situations for better treatment results.
AN OUNCE OF PREVENTION IS WORTH A POUND OF CURE
In addition to treatment, learn important principles of lifestyle, diet and exercise to optimize your health and prevent disease.
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION REPORTS:
Some diseases, symptoms or conditions for which acupuncture has been proved, through controlled trials, to be an effective treatment:
- Adverse reactions to chemotherapy
- Allergic rhinitis
- Arthritis
- Asthma
- Back pain
- Depression
- Gastritis
- Headache
- High blood pressure
- Induction of labour
- Infertility
- Insomnia
- Irregular or painful periods
- Knee pain
- Malposition of fetus
- Migraine
- Morning sickness
- Neck pain
- Stress
- Sciatica
This is a limited list so please call to find out if acupuncture therapy can address your health concerns.
Source: World Health Organization (WHO) / Review and Analysis of Reports on Controlled Clinical Trials


